How does L-Theanine relax us? Why is it that brain-scans show us that it puts us in the same state of mind as meditation? Why do bio-hackers often stack L-Theanine with caffeine?
In this article, I explain everything there is to know about this relaxing amino acid found in green tea.
Table of Contents:
- Quick Overview of L-Theanine:
- L-Theanine is the Relaxing Amino Acid Found in Green Tea
- Studies on Relaxation and Stress How L-Theanine Relaxes You by Boosting your GABA Levels
- Studies of L-Theanine Improving Attention and Reaction Times
- Studies on Memory and Learning
- L-Theanine Dosages
- L-Theanine and Caffeine, a Stack for Calm Focus
- The Verdict - Should You Try L-Theanine?
Quick Overview of L-Theanine:
- Benefits: For people needing to relax or want to socialise without feeling anxious, drinking green-tea boosts the same neurotransmitter as drinking alcohol... Without getting drunk.
- Actions: Alpha-brain waves and increases GABA production.
- Who is it good for? People who lack GABA tend to feel stressed and anxious. If you want to relax, L-Theanine is a natural de-stresser.
- Quality of studies: Good amount of human research mostly from Japan. 130 studies published on Pubmed.
- Time to effect: Within 40 minutes.
- Stacks with: Caffeine or Rhodiola Rosea for an energy and productivity boost (while staying relaxed thanks to L-Theanine).
- Recommended dose: 200-300mg per day. If you are taking it with Caffeine, maintain a 2:1 ratio e.g. Combine 100mg of Caffeine with 200 mg of L-Theanine.

L-Theanine is the Relaxing Amino Acid Found in Green Tea
Japanese green tea is famous for its relaxing properties. For thousands of years, Japanese emperors, samurais, and now office executives have been drinking it to wind down after a hard day's work.
Only recently have scientists discovered that L-Theanine is the source of Japanese green tea's relaxing qualities.
Studies on Relaxation and Stress
1. A double-blind human study found that "L-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses." (Nagoya University Department of Psychology - 1)
2. A group of 56 healthy young physicians saw improvements in mental fatigue, concentration and memory (Armenian State Medical University - 2)
3. A group of 18 "high stress" university students were given L-Theanine and produced Alpha waves. improved in reaction times and had decreased heart rates (University of Shiga Prefecture - 3)
4. "Animal neurochemistry studies suggest that L-theanine increases brain serotonin, dopamine, GABA levels" - in other words, it increases the release of the pleasure, motivation and relaxation neurotransmitters. (Monash University, Australia - 4)
5. Within just 40 minutes of taking L-Theanine, human volunteers produced alpha brain waves, "signifying relaxation without causing drowsiness". (The University of Shizuoka - 5)
6. Alpha waves are associated with a relaxed, attentive and calm state of mind. (Technical University of Graz - 6)
7. 400mg of L-Theanine daily for 8 weeks saw human volunteers "able to reduce anxiety and activation symptoms without significantly affecting quality of life or general functioning." (Israel Institute of Technology - 7)
How L-Theanine Relaxes You by Boosting your GABA Levels
So how does L-Theanine actually work to relax us? Let's take a deep dive into the neuroscience.
Too Many Excitatory Neurotransmitters Causes Anxiety
Neurotransmitters are our "chemical messengers." Whenever we think, or feel something, our brain-cells use neurotransmitters to send this information to each other... All the way around our brain. This is the current model of how our cognition works.
Most neurotransmitters are excitatory. That means they excite you or stimulate you into thinking or feeling something. e.g. Dopamine, your motivation neurotransmitter and Adrenaline, your fight or flight neurotransmitter. When these are released, you feel more of something.
The problem is when your neurotransmitters keep firing irrationally
You may have predicted the problem already. Too many excitatory neurotransmitters being released = anxiety and stress. Remember the last time you were anxious? You may have felt that sensation of "overthinking" everything.
"What are they thinking?" or "What do I do next?" or "X, Y, Z". Your brain is literally in excitatory neurotransmitter over-drive.
GABA to the Rescue, Your Primary Inhibitory Neurotransmitter
A healthy brain has ample amounts of an inhibitory neurotransmitter called GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid). Inhibitory is the opposite of excitatory. Instead of making you think more, inhibitory neurotransmitters make you think less.
Like a traffic warden, GABA limits the flow of neurotransmitters. Too much adrenaline? Zap. GABA puts the red light on and your adrenaline messages of "fight or flight" stop.
We can see a relaxed brain as indicated by "alpha brain waves" in brain-scans. These brain-waves measure how fast electricity is flowing around our brains. A state of "alpha waves" is similar to that of meditation; calm and awake.
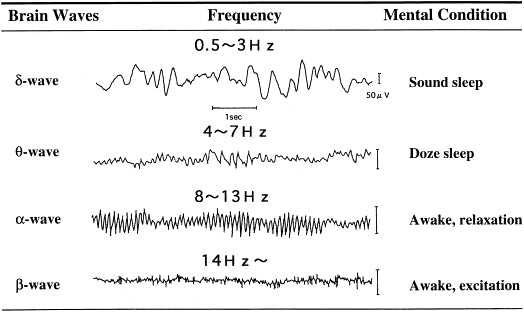
Anxious People Lack GABA
For people with low GABA, this unregulated "overthought" is what causes anxiety. The worst thing is that it's irrational. We're not stupid - we know that standing in the waiting line at Starbucks is not a threatening experience. Doesn't matter. Our lack of GABA means that adrenaline is flying through our brains and we enter "fight or flight" mode.
L-Theanine reduces anxiety by boosting the production of your GABA neurotransmitter
L-Theanine, Japanese Green Tea and even alcohol boost the production of our GABA neurotransmitter. That may explain why you like a drink or two after work. I certainly did - and it's because I couldn't "switch off" thinking about my to-do list.
Studies of L-Theanine Improving Attention and Reaction Times
If your'e stressed, you can't focus or pay attention. Studies show us that L-Theanine works very well to improve overall mental performance - likely as a result of relaxing our minds:
1. A human study stated: "Results evidently demonstrated that l-theanine clearly has a pronounced effect on attention performance and reaction time response in normal healthy subjects prone to have high anxiety." (University of Shiga - 8)
2. Combining L-Theanine with Caffeine "led to faster simple reaction time, faster numeric working memory reaction time, and improved sentence verification accuracy." (Northumbria University - 9)
3. Improved delayed recognition and immediate recall scores when combined with green tea extract (Park SK et al. - 10)
Studies on Memory and Learning
L-Theanine is not a "powerful" memory enhancer like the Choline supplements Alpha GPC or CDP Choline. Nonetheless, it's ability to de-stress and relax people has been seen to improve their attention and ability to recall information.
1. A human study stated: "Results evidently demonstrated that l-theanine clearly has a pronounced effect on attention performance and reaction time response in normal healthy subjects prone to have high anxiety." (University of Shiga - 8)
2. Improved delayed recognition and immediate recall scores when combined with green tea extract (Park SK et al. - 10)
L-Theanine Dosages
If you are particularly stressed, the research suggests that taking 200mg of L-Theanine will have a significant relaxing effect.
Here is a quote from a study of 18 "high stress" individuals being treated with 200mg at the University of Shiga Prefecture, Japan (8):
"Results evidently demonstrated that l-theanine clearly has a pronounced effect on attention performance and reaction time response in normal healthy subjects prone to have high anxiety."
If you are stacking L-Theanine with caffeine, taking twice the amount of caffeine is a good dosage. e.g. 100mg of Caffeine and 200mg of L-Theanine. This will take the edge off of the coffee.
L-Theanine and Caffeine - a Stack for Calm Focus
L-Theanine works fantastically well with stimulants. It's known to take the "edge off" caffeine (or Rhodiola Rosea), which balances out their anxiety-inducing side-effects.
It's essential to not get overstimulated in order to stay in the "focus zone." If you remember the last time you drank too much coffee, you may have felt "scatter-brain." This is the Yerkes-Dodson law - a decent amount of stimulation is great for attention and focus, but too much causes you to crash.

As above, I'd recommend taking a 2:1 ratio if you're stacking L-Theanine with Caffeine. An average cup of coffee contains about 100mg of Caffeine, so take 200mg of L-Theanine to go with it.
Northumbria University found that combining L-Theanine with Caffeine “led to faster simple reaction time, faster numeric working memory reaction time, and improved sentence verification accuracy.” (Northumbria University - 9)
The Verdict - Should You Try L-Theanine?
In my opinion, anybody feeling overly anxious and tends to overthink probably lacks the GABA inhibitory neurotransmitter. These people can benefit from taking either L-Theanine or drinking Japanese Green tea, since they're essentially the same thing.
If you're looking for a popular productivity stack, also try L-Theanine + Caffeine or L-Theanine + Rhodiola Rosea.
References:
- Nagoya University Department of Psychology - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16930802
- Armenian State Medical University - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11081987
- University of Shiga Prefecture - http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464611000351
- Monash University, Australia - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17182482
- The University of Shizuoka - http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924224499000448
- Technical University of Graz - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1376667
- Israel Institute of Technology - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21208586
- University of Shiga - https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464611000351
- Northumbria University - https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301051107001573
- Park SK et al. - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21303262




Leave a comment (all fields required)